Wild Deer
In the 19th Century, deer were imported to Australia from Europe as 'game animals.' Species of deer are otherwise native to all other continents, except Antarctica. There are six known species of wild deer in Australia: fallow, red, chital, hog, rusa and sambar.
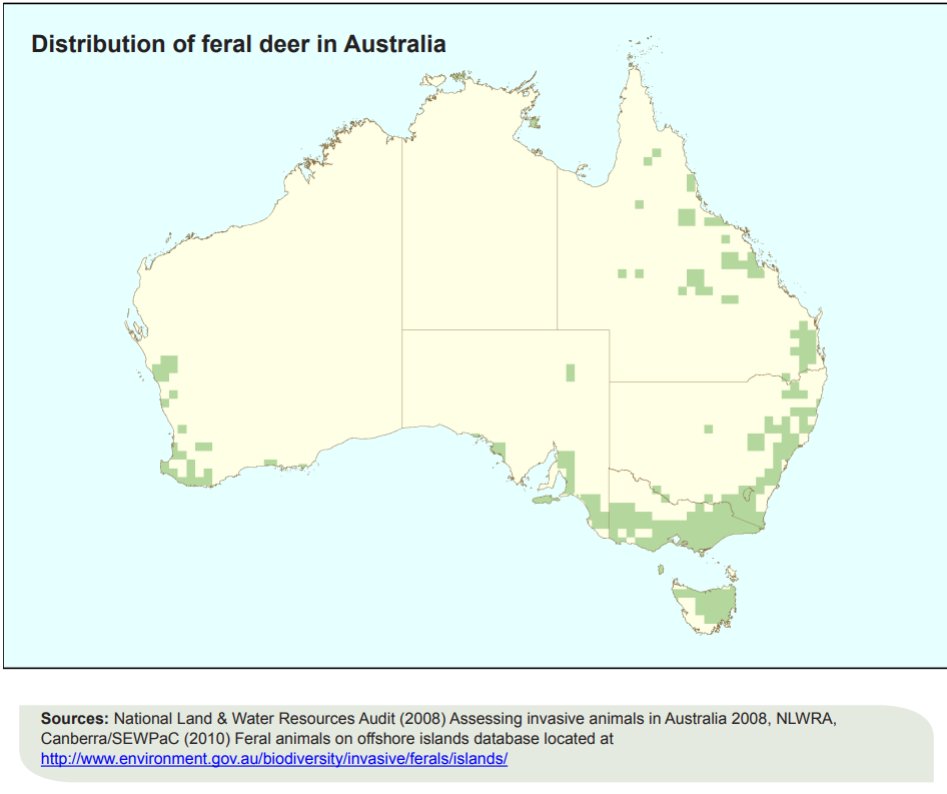
In 1995, only four populations of red deer were known in Australia but by 2007, 65 red deer populations had been identified. Wild populations have expanded, largely due to farmed deer escaping and breeding.
Wild deer management
Feral deer are considered competition to native species and to farmed animals, particularly cattle and sheep. As herbivores, they can also cause damage to crops and native flora.
Wild deer populations are largely concentrated in Victoria, however they are found in almost all states and territories. In QLD, deer were introduced in the 1800s and initially protected. That changed in 2009, when four species - chital, rusa, red and fallow deer - were declared pests.
The most common method of wild deer 'management' is shooting. Hunters will sometimes butcher and eat deer themselves, or give them to processors, who will sell them as wild venison.
For all species except Hog deer, in Victoria, there are no 'bag limits' on wild deer hunting.
Red deer, fallow deer, chital deer, rusa deer and sambar deer can be hunted all year round. However, the hound hunting of sambar deer can only take place from April - November each year. Hog deer can only be hunted durng the month of April.


